The Internet of Things (IoT) collects a vast amount of data, and businesses are putting this functionality to use. A growing number of IoT-enabled innovations are entering the market, from automated inventory management and connected supply chains, to scalable, customizable IoT cloud-based solutions for business.
And the pace is accelerating.
Over the past three years, the number of B2B IoT device connections has increased from 2.5 billion to 5.4 billion, and the economic value of the entire connected industry is estimated to be in the trillions each year.
While there are seemingly limitless new connected applications emerging across a variety of industries, the real value of the IoT lies in the data and the insights it’s capable of providing.
The power of data
“What people say and what people do are very different,” said Upchain in its post, IoT is Flipping Product Development on its Head.
And it’s true. For a variety of reasons, consumers often do things which seem counter-intuitive to what they say. For example, as Upchain pointed out, Ryanair experienced soaring stock value despite persistently poor reviews. How? People like dirt-cheap air fare, of course. Despite the poor lip service, wallets continued to open for cheap flights.
In the B2B realm, this truism begs the question: If we can’t trust our customer reviews, what can we trust? The answer is data.
In the race toward greater customer-centricity and reduced customer churn, the IoT wields the power of truth. Tracking customer attitudes and actions—and leveraging that data—is easier and more accurate today than ever before. This means opportunities for customer engagement at every business level are at an all-time high.
Let’s explore how.
IoT data improves and personalizes marketing and CRM
Customer engagement and connection are critical in marketing and customer relationship management (CRM). Most customers’ first interaction with a business will be with a marketing asset. After purchasing, communication and engagement typically fall to CRM.
Data harnessed by IoT technologies helps businesses design better customer-engagement tactics. For example, geolocation and usage data tells marketers where more potential customers may be located and how customers are using a product or service. This information informs marketing campaign targeting and messaging.
Usage data is also of great value for monitoring engagement. Decreased usage—or failure to take advantage of the full range of features in a product—may signal trouble. This kind of information should trigger communication, such as this email from collaboration tool Trello sent a few days after account activation.
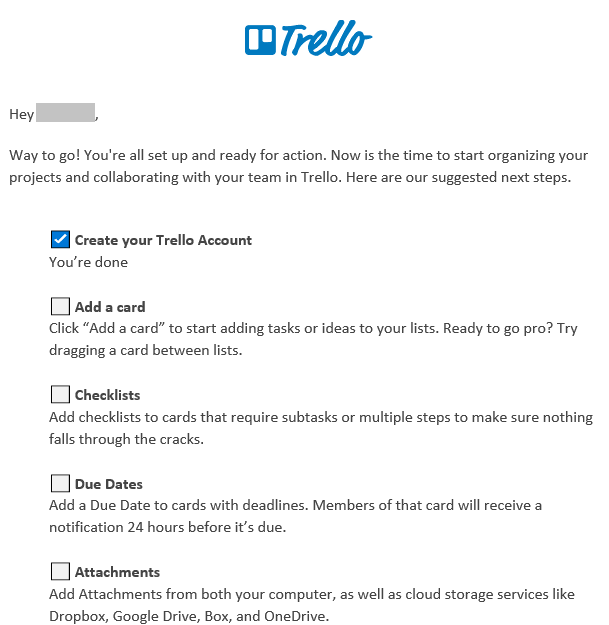
While likely automated, this communication offers a personal touch based on data indicating the new customer has yet to use many of the product’s features. This encourages customer engagement and increases the chances of retention, adding to customer lifetime value (CLV).
Examples of this IoT-enabled engagement abound, from HP Insta Ink’s ability to identify low printer ink levels and alert a customer that more cartridges are on the way, to segmenting marketing target audiences based on location, behavior, and more.
Accurate, real-time data provided by the IoT empowers businesses to connect with customers better than ever before.
A more informed sales team engages and connects more effectively
For many B2B businesses, a prospective customer appears thanks to marketing efforts, but stays because of the sales team. Sales is a critical part of the customer journey, and customer data is a key component of successful sales. Fortunately, the IoT has that covered.
Just as marketing leverages IoT data to segment target audiences, so too can sales use customer data to inform interactions with prospects. Imagine IoT sensors and analytics have detected that property managers in warm climates tend to request more maintenance on a basic air conditioning unit. In this scenario, sales can encourage prospects in those climates to consider a more robust unit requiring less attention, or cross-sell a maintenance service package.
Of course, sales works with existing customers as well. Noting an uptick in pages printed, an HP Insta Ink sales associate (or bot) might encourage a customer to upgrade to a higher plan to avoid spending more on printing overages.
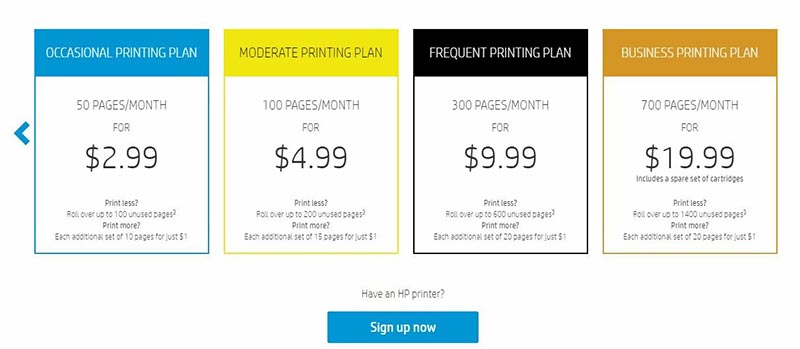
The IoT relays usage, maintenance needs, ink levels, and more in real-time. This paves the way to addressing issues as they occur, which increases customer satisfaction.
IoT data strengthens connection through product development
While development teams typically don’t interact with customers directly, product improvements do increase customer engagement and loyalty. Customer feedback, reviews, and the CRM team provide useful windows into trends and pain points.
Raw data gathered by IoT sensors reflects actual—rather than reported—usage, location, and more, which adds to the accuracy of this feedback.
The IoT gives developers a true picture of how products are used, enabling them to make development decisions based on real data. And better products, of course, mean a better customer experience.
Additionally, this kind of data informs development of aftermarket products and services based on trends identified by analysis. For example, if customers prefer to replace their own air conditioning filters, can replacements be designed to make the task easy? This also ties back into sales. If unit sensors detect and relay a need for a filter change or more comprehensive maintenance, sales can reach out accordingly.
Sensors indicating a need for maintenance or opportunities for more efficiency give a business the chance to optimize a product and improve the customer experience. Great experiences encourage engagement and build connection, creating long-lasting customer relationships.
The IoT strengthens B2B operational foundations
Businesses are using the IoT to enhance their transportation, maintenance, and inventory, and to ensure they’re engaging with their customers and operating at optimal levels of efficiency.
In the case of transportation and telematics, the IoT has enabled detailed vehicle tracking, optimized routing, and faster service provision when it comes to fleet management. This enables service vehicles, for example, to reroute based on live traffic updates and easily record tasks they complete on calls. What’s more, customers can see how close an approaching service vehicle is and get an accurate invoice generated by IoT sensors on the equipment used.
Consider GE Aviation, which set a new bar for customer-optimized product maintenance. Using the IoT to detect and alert its customers to their jet maintenance needs has reduced the time an engine spends being repaired. By increasing the amount of time a jet can spend in the air, GE built a stronger connection with its customers and earned more loyalty.
Clicksale automates inventory ordering for distributors with a simple button that orders and invoices simultaneously. Other IoT inventory pioneers have installed smart shelves that communicate ordering needs automatically to manufacturers. The information is also shared with shipping partners, including estimates of shipment size, date of delivery, and destination. All of this means product is available precisely when customers want it.
IoT as the future for B2B growth
Options for leveraging the power of IoT technology abound, from segmenting target audiences to keeping warehouse shelves full and even enabling unique IoT billing strategies. Additionally, the IoT continues to inspire innovation in business. Look no further than the success of big data leaders Facebook, Amazon, Alphabet (Google), Apple, and Microsoft for evidence.
For businesses seeking increased customer engagement, the IoT may not have all the answers—but it does have the data needed to find them.







